Since February 2024, services such as Gmail and Yahoo Mail require DMARC settings from senders. Especially those who send bulk messages and newsletters.
If you want to improve your mail delivery and increase the score of your emails for message recipients, you need to optimize your domain settings. Gmail or Yahoo mail servers will often evaluate email as SPAM because of one of these settings. In this tutorial, we’ll go over basic optimization and domain settings to keep emails coming in without any issues.
A free tool that can improve the rating of specific emails or reveal the reason for marking emails as SPAM is called Mail Tester. The tool checks the score of a particular email and provides suggestions on how to improve the delivery of emails by the sender.
SPF
A Sender Policy Framework (SPF) record is a type of TXT record that contains information about which SMTP servers (IP addresses) have permission to send e-mail from a particular domain. The goal of SPF is to limit sender spoofing in email and prevent SPAM.
How to set up an SPF record
If you are sending emails from Active24, the SPF record will look like this (may slightly differ for each domain):
v=spf1 and mx include:_spf.websupport.cz ?all
This record indicates that the SMTP server smtp.websupport.cz is authorized for the domain vasedomena.tld. If the IP address of the SMTP server from which the message was sent (smtp.websupport.cz) matches the SPF record, the message will be processed.
As soon as the message is sent via a foreign SMTP server, e.g. smtp.priklad.cz, the e-mail will lose points in its rating and will probably be evaluated as SPAM.
SPF is part of the TXT records, so you can set it in DNS > TXT records.

Combination of multiple SPF records
There must be only one TXT record for SPF in the DNS record. If you need to allow sending from multiple servers, you need to combine the SPF records into one.
For example, if you need to add a Google SPF record to our SPF record, here’s how to do it:
- original record: v=spf1 a mx include:_spf.websupport.cz ?all
- new record: v=spf1 a mx include:_spf.websupport.cz include:_spf.google.com ?all
Entries are separated by spaces. The SPF records in our example have authorized Active24 and Google servers. Other servers are not authorized and will not pass the SPF check.
DKIM
DKIM (DomainKeys Identified Mail)- authorization of sent emails using a signature is enabled by default on the hosting. In this case every email from our servers is authenticated.
How to set up DKIM
První krok je zapnutí ověřování emailů pomocí DKIM, které je možné zapnout/vypnout na úrovni celé domény.
- Log in to WebAdmin
- Go to the Services section and click on the desired domain.
- Click on the Emails section in the left menu
- Go to Domain security
- In the DKIM section, you can select from the list the option of setting on or off

The second step is to add DKIM to the domain’s DNS records. DKIM is added automatically after successful domain registration or transfer, within 24 hours. You can find it in the records in the TXT records category.

If DKIM is not visible in the list of TXT records, you can add it:
- In the left menu under the domain, go to DNS section
- Click on Quick Settings
- Click on Websupport Mail – you will see the name starting with: mail._domainkey in the records overview.
- If you have set up our NS records, just click Continue and the record will be added automatically.
If you are using different NS records, copy this record and add it to your TXT records.
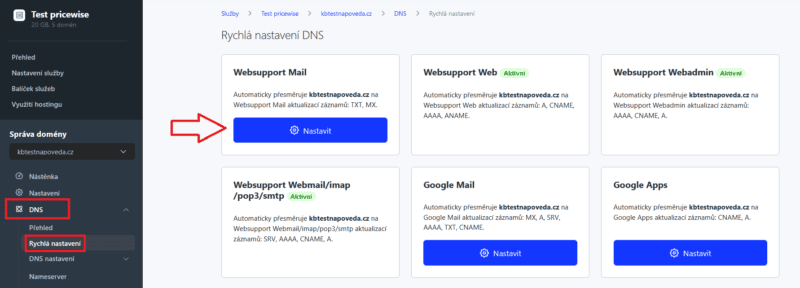

If DKIM is not visible in the quick settings, please contact our support.
DMARC
DMARC is a specification that allows you to combine the two authorization technologies SPF and DKIM to inform the recipient server what rules to apply to messages from a given domain.
DMARC builds on and combines these two technologies and has the following key features:
- Based on the sender address specified in the From header of the email, it tries to verify that the email was actually sent from that domain.
- Uses SPF and DKIM – if SPF has been met by the sender domain or the email carries a verified DKIM key, it considers the message trusted
- Defines a policy for failed emails – how to handle those that fail DMARC verification
- Allows you to set up feedback – where and how to send DMARC result messages for emails (supposedly) sent from a given domain
- You can set it to apply to only a subset of emails and deploy them gradually
- The DMARC is published by the sending domain holder and authenticates the recipient of the email
DMARC is not just a stand-alone technology, it builds on existing SPF and DKIM. These are used by recipients to verify whether an email has passed the rules for sending from a domain according to mail from SMTP and from which domain it has valid signatures. This information is then sent to the DMARC module, which compares and examines whether domains verified in SPF or DKIM have anything in common with the From header. If at least one part is true, the DMAR says it can be trusted that the email was indeed sent from that domain.
As of February 2024, email service providers such as Gmail and Yahoo are required to senders who send bulk emails to have a DMARC record set up in addition to SPF and DKIM.
How to set up DMARC
DMARC is activated by adding a DNS record of type TXT
Address: _dmarc
Text: v=DMARC1; p=none; rua=mailto:reporty@vasedomena.tld
TTL: 3600
Within DMARC, you can set several parameters that govern its management.
„v“ – version of the protocol, currently only DMARC1 is used
„p“ – the required action of the recipient, i.e. how the recipient should handle a message that has failed the SPF and DKIM checks. The options are:
none – the recipient takes no action, performs a standard SPF and DKIM check and uses these to determine the trustworthiness of the message and processes it according to its own rules
quarantine – the recipient receives a message marked for quarantine and handles it according to his/her own rules, e.g. moves it to junk mail
reject – the recipient in this case refuses delivery of the message, so the message does not reach the destination mailbox at all
„rua“ – email address for sending aggregated reports on whether any emails sent from your domain have failed DMARC checks.
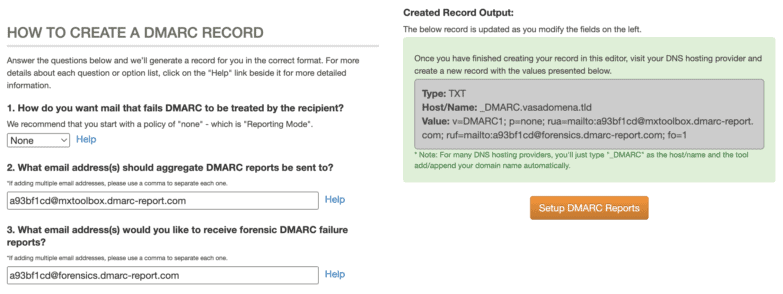
Generating a record through mxtoolbox
If you don’t want to get confused when setting up a DMARC record, it can be easily generated on the MX Toolbox website.
- Go to the page MX Toolbox.
- You enter the domain name and click on „Check DMARC record“.
- On the left side you set the individual parameters according to the listing above and on the right side the DMARC is automatically updated according to the parameters entered.
Copy the finished “Suggested record” and create a new TXT record in Webadmin. If you haven’t created a TXT record yet in our administraton, use this tutorial.
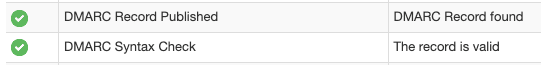
You can also use the MX Toolbox to verify that the DMARC you created is correct.
Other recommendations
Other criteria such as attachment size, textual content, functionality of URL links, etc. are also included in the evaluation of the email. The free tool on the Mail Tester page, which also tests the content criteria of the email, can help you with the setup.
Further recommendations for improving deliverability can also be found in an article by Sendgrid.
